With its dark body and intricate shiny keys, and its warm tone, the clarinet is one of the most popular instruments today. It is relatively easy to learn and very versatile in the genres it is able to play.
From its long history to its composition, there are many interesting facts about the clarinet that few people know but every music enthusiast should learn! Let’s take a look at some of them.
1. Descended From the Chalumeau

As with many instruments we are familiar with today, the clarinet was a modification on an older instrument called the Chalumeau.
The chalumeau was a wooden reeded folk instrument played during the Baroque and Classical periods that had two keys and eight tone holes.
Part of the motivation to develop the clarinet was the addition of an upper register by way of an overblow key, a key that you press to open an airway in the instrument allowing certain notes to be played between one octave and 12 notes higher.
When looking at the history of the clarinet, it is widely believed that Johann Christoph Denner invented the first clarinet in the mid 1600s although his brother Jacob is also credited.
2. The Evolution of Keys
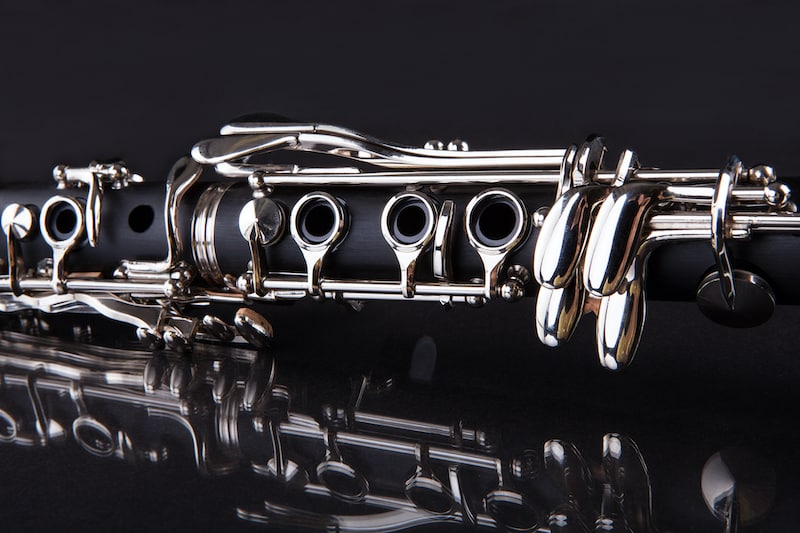

The earliest clarinet developed straight off of the chalumeau also only had two keys.
A larger bore and flared bell were two additional differences between the first clarinet and the chalumeau.
What really characterises the clarinet’s development since then is the progressive addition of keys.
Between 1730 and 1740, a couple of different clarinet crafters (including one of Denner’s sons) added a third key to the clarinet.
This key allowed for play between the lower chalumeau register and the upper new registers of the first clarinets.
These clarinets also played primarily in the keys of C and D.
Over the next hundred years, more and more keys were added to the clarinet.
With each addition, clarinetists could achieve new registers, better tone quality, and more dynamic fingering options.
In 1843, the world saw the first 17-key B flat clarinet similar to the one we know now.
3. Each Register Has Its Own Name
The clarinet can play in three full registers, which each has its own name.
We have already covered the altissimo register, which is the higher register that was added when the chalumeau transformed into the clarinet.
This is still the highest of the clarinet’s registers, and it ranges from a high C sharp to the clarinet’s highest note, a high A sharp.
The lowest register is referred to as the chalumeau register, as this was the register the chalumeau was able to play in.
It ranges from the clarinet’s lowest note, a low D, to a middle A.
The middle B through the high C are known as the clarion/clarino register.
The clarion/clarino was an ancient ancestor of the trumpet, and this register range is similar to the trumpet’s main register range.
Clarinet also means small clarion/clarino, so the clarinet is also related to the trumpet, predominantly in terms of the bell shape and the acoustics it creates.
4. An Extensive Family Tree
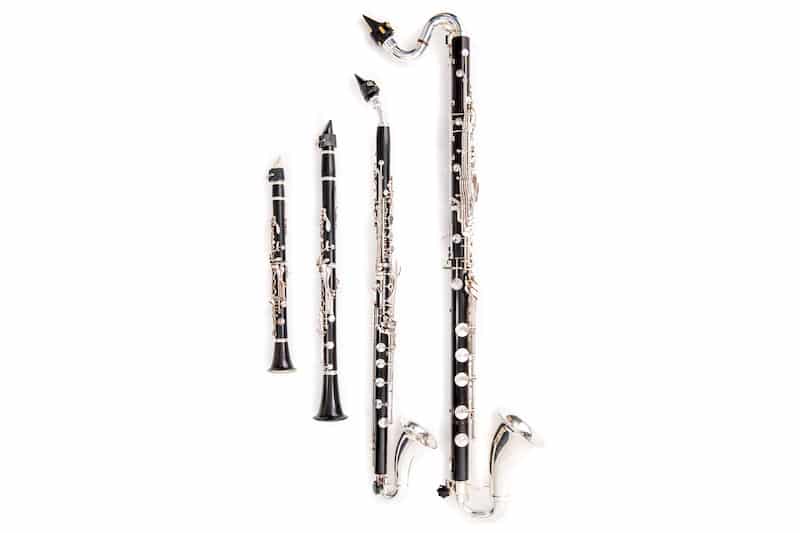

The clarinet family is large and diverse, playing a very important role within the larger woodwind family.
The clarinet most commonly played and showcased is the B flat clarinet which is also the instrument that the vast majority of new clarinetists start on.
The B flat clarinet is also known as the soprano clarinet due to its tonal range but there are several clarinets built to play in various other keys.
Clarinetists use these different types to adapt play to specific pieces.
For example the E flat and A clarinets are the two most commonly used for this purpose today and they are also considered to be soprano clarinets.
The D and C clarinets are very early versions of the clarinet that are sometimes used today when playing music from their eras for a more historically authentic sound.
The G clarinet is built in the Albert keywork system, a system of fingering designed specifically for ethnic and folk music.
Also known as the Turkish clarinet because it was originally created in Turkey, this clarinet is most commonly produced and played today in China.
There are also members of the clarinet family designed to expand upon the B flat clarinet’s registers.
The E flat alto clarinet is pitched down to, you guessed it, low E flat, or a fifth below the B flat clarinet’s lowest register note.
More common is the B flat bass clarinet, playing an octave below the traditional B flat clarinet.
Although very uncommon, there are also still A and C bass clarinets in existence.
The contrabass B flat clarinet plays an additional octave below the B flat bass, and the contra-alto an octave below the alto.
Although very uncommon due to the sound being undesirable except for in very specific circumstances, there is also an A flat piccolo clarinet that plays an octave above the B flat’s altissimo register.
5. The Clarinet’s Most Common Music Genres
The clarinet is a very versatile instrument, and therefore plays unique roles in many different genres of music.
It is showcased in a lot of Classical music, as its greatest development took place during this era in order to expand its range on account of its growing popularity.
While today the clarinet is a standard player in every orchestra, it was actually one of the last instruments to be added to orchestral ensembles.
Orchestral music dates back to the early 1600s, but the clarinet was not added and developed as mentioned above until the 1700s.
Even today, there are only a few clarinet chairs in even the largest orchestras.
The early 1900s brought the birth of Dixieland jazz, which combined the ragtime, military brass band, blues, and gospel genres and the clarinet was a key player in the movement.
Then, in the 1930s and 1940s, the clarinet was part of the Swing music movement with players like Benny Goodman popularizing the instrument even more.
During the 1950s and 1960s, the clarinet was an instrumental (no pun intended) part of Jazz music’s boom in popularity and fusion with other music genres.
Most movie scores are composed for orchestral ensembles, and while the clarinet parts are few as mentioned previously, they are nonetheless crucial.
6. Famous Solos
Within each of the aforementioned genres, there are some very famous clarinet solos to note.
Mozart and Copland both wrote clarinet concertos that almost every clarinetist is exposed to at some point in their musical journeys.
But, perhaps the most famous clarinet solo of all is its introduction to Gershwin’s Rhapsody in Blue.
This is one of the most difficult clarinet solos in existence on account of that characteristic glissando, created by sliding the fingers over the finger holes at exactly the right pace, in perfect unison, and simultaneously tightening the throat just enough.
7. Famous Clarinetists
After reviewing the clarinet’s most famous solos, it is also important to note its most famous players.
King of Swing Benny Goodman is arguably the most well-known clarinetist in the world. He was also a popular bandleader who is bestowed with a great deal of credit for the Jazz revolution.
The most famous classical clarinetists include Martin Frost of Sweden and Sabine Meyer of Germany.
Well before the time of Frost and Meyer, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart was not only a famous composer but fell in love with playing and composing for the clarinet in particular.
Jazz soloist Eric Dolphy is considered by many to be the most famous bass clarinetist.
Related: For more, check out our list of famous clarinet players here.
8. Clarinets Have Been Made from Various Materials
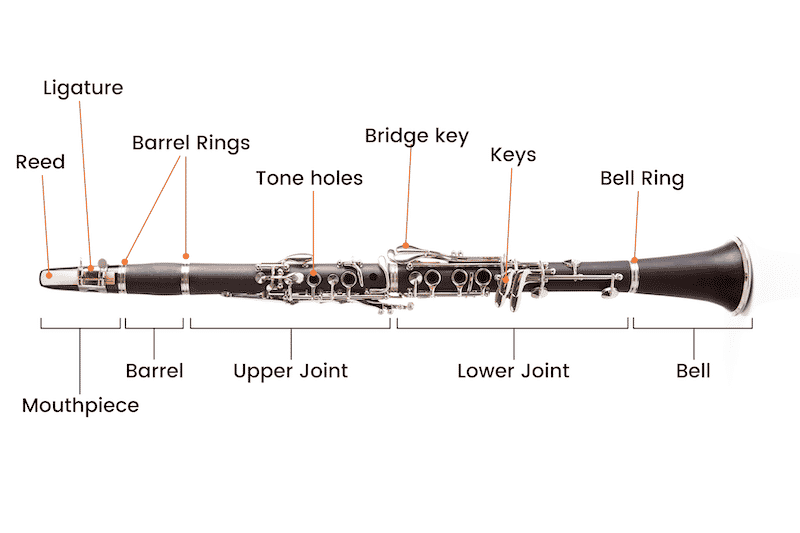
True to its woodwind category, most of the clarinet’s parts are and have always been made from wood.
The earliest clarinets were most commonly composed of boxwood, pear wood, or plum wood, with some rare early instruments being made of ivory, and the mouthpieces were typically comprised of ebony.
Today, the highest quality clarinets are made of African blackwood or grenadilla wood, also native to Africa.
There is some controversy in the music community surrounding this, as both types of wood are becoming endangered.
Many manufacturers are therefore branching out to other types of wood and even other materials like metal, rubber, resin, and even plastic which are also very common among beginners and more affordable models.
Most modern mouthpieces are also made of plastic.
9. Most Affordable Woodwind Instrument
While on the topic of affordability, the clarinet is one of the cheapest woodwind instruments to learn and play.
The best beginner clarinets can be purchased for less than $500, and professional-level models can be found in the $2000 range.
Given their small size, the clarinet reed is also the cheapest of all the woodwind reeds, costing an average of $2 per reed.
10. No Spit Valve
If you have ever played the clarinet or watched a clarinetist, you have seen the tell-tale puddle of spit that accumulates directly below the bell.
Whereas brass wind players can control where their spit goes by releasing it through their spit valves, the vertical and open nature of the clarinet’s body leaves the clarinetist no choice but to let it all drip freely.
On the plus side, this means that clarinets are not burdened with keeping tabs on how accumulating saliva affects their sound.
However, never forget to run your spit rag thoroughly through your clarinet after every play to take care of the condensation left behind!
Taking aspects from the earliest woodwinds and the trumpet, the clarinet has become a unique addition to the music world.
Thanks to its enormous family tree and careful design during the 1700s and 1800s, as well as its popularity among musical greats, the clarinet has become a star player in many music genres and famous pieces.
Summing up Clarinet Facts
Anyway, that’s it for our list of clarinet facts, we hope you learned something new!
Hopefully, they will inspire you to pick one up and play or tune into a famous clarinet solo today.
If you have any other interesting facts for us to include, let us know and we’ll add them to our list.

